หลังจากที่เราได้ทดลองทำโปรเจกต์ Hello World ผ่านสิ่งต่างๆไปมากมายแล้ว หากใครเริ่มศึกษาเรื่อง Web Programming ก็น่าจะเคยได้ยินคำว่า Protocol บ้าง แต่หลายคนอาจจะยังไม่รู้จักว่ามันคืออะไร ในบทความนี้เราจะมาพูดถึงเจ้า Protocol นี่กันครับ แต่ก่อนอื่นผมขออธิบายเกี่ยวกับ Computer Network สำหรับผู้ที่ยังไม่มีพื้นฐานก่อนนะครับ ใครรู้อยู่แล้วก็ข้ามไปได้เลย
Computer Network แปลเป็นภาษาไทยได้ว่า “เครือข่ายคอมพิวเตอร์” หมายถึงระบบการนำเครื่องคอมพิวเตอร์หลายๆเครื่องมาเชื่อมต่อกัน ทำให้สามารถรับส่งข้อมูลระหว่างกันหรือใช้ข้อมูลร่วมกันได้ กรณีที่เราพบได้บ่อยๆคือการเชื่อมต่อคอมพิวเตอร์หลายๆเครื่อง (Client) ไปที่คอมพิวเตอร์ที่เป็นศูนย์กลาง (Host) เริ่มเห็นภาพหรือยังครับ? ถ้ายังนึกไม่ออกก็ขอให้อ่านต่อครับ
สมมติว่าเรามีคอมพิวเตอร์สองเครื่องและต้องการจะให้สองเครื่องนี้ติดต่อสื่อสารกันได้ สิ่งที่เราต้องทำคือเชื่อมต่อระหว่างสองเครื่องนี้ด้วยสาย Ethernet หรือ WIFI หรือ Bluetooth เป็นต้น การทำเช่นนี้คือ network แบบง่ายๆครับ แต่ถ้าเรามีคอมพิวเตอร์จำนวนมากขึ้น เช่น มีคอมพิวเตอร์ 10 เครื่อง เราต้องใช้สาย 45 เส้นเพื่อจะเชื่อมต่อให้ครบทุกคู่ แค่คิดก็มึนแล้วใช่ไหมครับ วิธีแก้ก็คือเพิ่มคอมพิวเตอร์เล็กๆชื่อว่า router ขึ้นมา 1 ตัว แล้วให้ทุกเครื่องมาเชื่อมต่อกับ router แทน เราก็จะใช้สายแค่ 10 เส้นเท่านั้น ส่วน router ก็ให้ทำหน้าที่คล้ายนายสถานีคอยสับรางให้ข้อมูลที่แต่ละเครื่องส่งมาไปถึงผู้รับที่ถูกต้อง เช่น เครื่อง A ต้องการส่งข้อมูลให้เครื่อง B นายสถานี Router ของเราก็ต้องสับรางให้วิ่งจากเครื่อง A ไปเครื่อง B ไม่ใช่สับไป C, D, E, … นะครับ
แต่ถ้าเรามีคอมพิวเตอร์เยอะขึ้นอีกล่ะ แน่นอนว่าถ้าจำนวนมากเกินไป router ตัวเดียวคงจะสับรางหรือทำงานให้เราไม่ไหว แต่ในเมื่อ router ก็คือคอมพิวเตอร์ตัวหนึ่ง ดังนั้นมันจึงเชื่อมต่อกันเองได้ สิ่งที่เราจะทำเมื่อคอมพิวเตอร์มีจำนวนเยอะขึ้นก็คือแบ่งกลุ่มคอมพิวเตอร์ให้ต่อ router แต่ละตัว แล้ว router แต่ละตัวก็มาเชื่อมต่อกันอีกที กลายเป็น network of networks ซึ่งถ้าสเกลใหญ่ขึ้นอีกเป็น worldwide network of networks ก็คือ Internet นั่นเองครับ
Internet เป็น worldwide network of networks ที่ใช้ Internet protocol suite หรือที่เรียกกันว่า TCP/IP ซึ่งเป็นชุดของ Protocol ที่มีความสำคัญมากในการติดต่อสื่อสารกัน ว่าแต่ Protocol คืออะไรกันนะ?
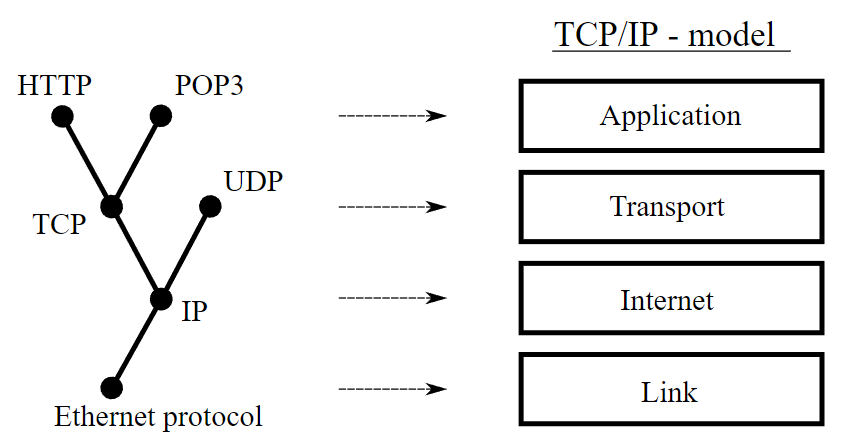
Protocol คือ ชุดของกฎหรือข้อตกลงในการสื่อสารระหว่างคอมพิวเตอร์หรือภายในคอมพิวเตอร์ โดยจะกำหนดรูปแบบและขั้นตอนในการติดต่อแลกเปลี่ยนข้อมูลกัน ซึ่งทั้งต้นทางและปลายทางจะต้องทำตามกฎนี้เป๊ะๆจึงจะสามารถรับส่งข้อมูลกันได้ การออกแบบ Protocol ในสมัยใหม่จะแบ่งเป็นชั้นๆ (layer) ตัวอย่าง TCP/IP model หรือ Internet จะมีลักษณะดังในภาพนี้[7]
คราวนี้เรามารู้จัก Protocol ที่สำคัญกันดีกว่าครับ
TCP เป็น network protocol ที่สำคัญตัวหนึ่งในระดับ Transport Layer ทำหน้าที่จัดการควบคุมการรับส่งข้อมูล โดยอนุญาตให้ host สองตัวติดต่อและแลกเปลี่ยนข้อมูลแบบต่อเนื่องกัน ในกรณีที่ข้อมูลมีขนาดใหญ่ TCP จะเป็นตัวจัดการแยกข้อความหรือไฟล์เป็นส่วนเล็กๆเรียกว่า message แล้วส่งไปยังผู้รับ จากนั้นจึงประกอบกลับให้เหมือนเดิม โดยรับประกันว่าการส่งข้อมูลและ packet จะถูกต้องตามลำดับเหมือนกับที่มาจากผู้ส่ง นอกจากนี้ยังควบคุมการไหลของข้อมูลไม่ให้เร็วเกินไปจนผู้รับรับไม่ทันด้วย
TCP ถูกออกแบบโดย Vint Cerf และ Bob Kahn ช่วงคริสต์ทศวรรษ 1970 ซึ่งตอนนั้นพวกเขาเป็นนักวิทยาศาสตร์ของ DARPA
IP เป็น protocol ในระดับ Network Layer ทำหน้าที่จัดการเรื่อง address ของแต่ละชุดข้อมูลตาม IP address ที่อยู่ใน packet header โดย IP จะหาเส้นทางที่ดีที่สุดในการส่งข้อมูลซึ่งในการเชื่อมต่อแต่ละครั้งเส้นทางก็อาจจะต่างกันก็ได้ เวอร์ชันหลักของ IP ได้แก่
FTP เป็น protocol มาตรฐานที่อยู่มานานมากๆครับ สร้างโดย Abhay Bhushan เผยแพร่ครั้งแรกในปี 1971 ใช้สำหรับส่งไฟล์จาก host ผ่านทาง Internet ถึงแม้ในปัจจุบันผู้พัฒนาหลายคนและ host หลายเจ้าจะไม่อนุญาตให้ใช้ FTP โดยให้ใช้ระบบ Version Control เช่นพวก Git แทน แต่เราก็ยังสามารถพบการใช้งาน FTP ได้ในระบบ host เก่าๆอยู่ครับ
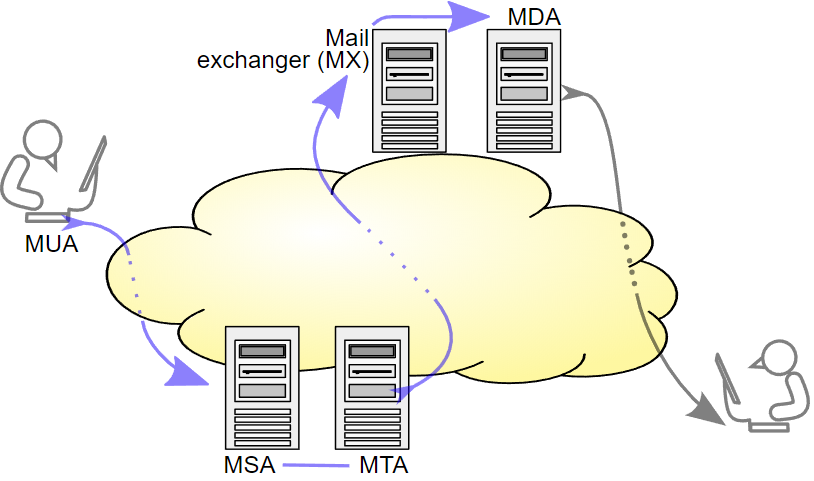
SMTP เป็น protocol ที่ใช้สำหรับส่งอีเมล สร้างโดย Ray Tomlinson เผยแพร่ครั้งแรกในปี 1981 ลักษณะการทำงานของ SMTP คือ เมื่อผู้ใช้งาน (MUA, mail user agent) ส่งอีเมลไปที่ mail server (MSA, mail submission agent) โดยใช้ SMTP บน TCP port 587 หรือ port อื่นๆที่ใช้ได้ MSA จะส่งเมลไปที่ mail transfer agent (MTA) ซึ่งโดยทั่วไป MSA และ MTA มักจะเป็น software ตัวเดียวกันอยู่ในเครื่องเดียวกัน กรณี MTA มีหลายเครื่องก็จะส่ง message ระหว่างกันโดยใช้ SMTP จากนั้น MTA จะใช้ DNS (Domain name system) ดู mail exchanger (MX) record ของโดเมนผู้รับ (คือส่วนที่อยู่ทางขวาของสัญลักษณ์ @ ในชื่ออีเมล) แล้วจึงติดต่อกับ exchange server ในฐานะ SMTP client หลังจากได้ message ครบแล้วก็จะส่งต่อให้ mail delivery agent (MDA) ซึ่งอาจจะส่งต่อให้ Local Mail Transfer Protocol (LMTP) ด้วย SMTP หรืออื่นๆ อย่างไรก็ตามสุดท้ายปลายทางก็จะเก็บ message ไว้ที่ local mail server สรุปขั้นตอนคร่าวๆได้ดังภาพ[10]
ประโยชน์ของ Protocol คือทำให้คอมพิวเตอร์ทุกค่ายทุกรุ่นในโลกนี้ติดต่อสื่อสารและแลกเปลี่ยนข้อมูลกันได้ครับ สำหรับในธุรกิจการที่คอมพิวเตอร์สามารถแลกเปลี่ยนข้อมูลหรือใช้ข้อมูลร่วมกันได้จะทำให้เราสามารถประหยัดทรัพยากรหรือค่าใช้จ่ายในระบบของเราไปได้มากครับ ตัวอย่างที่เห็นได้ชัดๆก็เช่น โดยทั่วไปแทบทุกบริษัทต้องมีการพิมพ์เอกสารใช่ไหมครับ ทีนี้ถ้าเราไม่มีระบบที่เชื่อมคอมพิวเตอร์ทุกเครื่องไว้ด้วยกัน เราอาจจะต้องมีเครื่องปริ้นท์เท่าจำนวนพนักงาน หรือต้องเอาข้อมูลเอกสารใส่ Thumb drive แล้วมาเสียบเครื่องปริ้นท์ทีละคน ซึ่งก็คงไม่เข้าท่าและเสียเวลาน่าดู แต่ถ้ามีระบบที่เชื่อมต่อกันหมด พนักงานแต่ละคนก็จะสามารถสั่งพิมพ์ได้จากเครื่องตัวเองเลยซึ่งสะดวกกว่ามาก
หรืออีกตัวอย่าง สมมติบริษัทของเรามีขนาดใหญ่ก็ย่อมต้องมีข้อมูล เช่น ข้อมูลของลูกค้า หรือสินค้า เก็บไว้ ซึ่งข้อมูลพวกนี้แหละครับ สมควรเป็นอย่างยิ่งที่จะต้องเป็นข้อมูลที่อยู่ในเครื่องส่วนกลางที่ทุกคนสามารถเข้าไปดึงข้อมูลมาใช้ได้ เพื่อให้ข้อมูลที่ได้เหมือนกันทั้งบริษัทและสามารถค้นหาได้อย่างรวดเร็วครบถ้วน ไม่ใช่เก็บไว้เครื่องใครเครื่องมันแล้วเวลาจะใช้ก็หาไม่เจอหรือเจอข้อมูลเก่าที่ไม่ได้อัปเดท
สุดท้ายนี้ถ้าผู้อ่านอยากเรียนรู้เรื่องเกี่ยวกับ Web Programming อย่างลึกซึ้งก็ขอแนะนำคอร์ส Web Programming ของทาง EPT ครับ สามารถดูรายละเอียดคอร์สได้โดยคลิกที่นี่หรือติดต่อได้ที่ 085-350-7540
แล้วพบกันใหม่บทความหน้าครับ
[1] https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Learn/Common_questions/How_does_the_Internet_work
[2] https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Glossary/protocol
[3] https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Glossary/Internet
[4] https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Glossary/TCP
[5] https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Glossary/IPv4
[6] https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Glossary/IPv6
[7] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Communication_protocol
[8] https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Glossary/FTP
[9] https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Glossary/SMTP
[10] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Simple_Mail_Transfer_Protocol
Tag ที่น่าสนใจ: protocol computer_network tcp ip ftp smtp internet_protocol transmission_control_protocol file_transfer_protocol simple_mail_transfer_protocol internet network_layer transport_layer tcp/ip network_of_networks
หากมีข้อผิดพลาด/ต้องการพูดคุยเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับบทความนี้ กรุณาแจ้งที่ http://m.me/Expert.Programming.Tutor
085-350-7540 (DTAC)
084-88-00-255 (AIS)
026-111-618
หรือทาง EMAIL: NTPRINTF@GMAIL.COM
