webpack คือ static module bundler สำหรับ JavaScript Application หรือก็คือตัวรวม module ย่อยๆที่เราเขียนเข้าด้วยกันทำให้ได้ไฟล์ที่สามารถใช้งานได้จริง ถ้านึกภาพไม่ออกให้ลองดูตัวอย่างในหัวข้อต่อไปนี้ดูครับ
สมมติว่าที่บ้านเราเปิดร้านอาหารที่กำหนดให้ลูกค้าซื้อได้แค่คนละ 2 รายการเท่านั้น และร้านเราก็มียอดขายในแต่ละวันสูงมากจะต้องคิดภาษีมูลค่าเพิ่ม เราก็เลยขี้เกียจกดเครื่องคิดเลขทีละใบเสร็จ เลยตัดสินใจจะทำ Application เพื่อใช้สำหรับคำนวณภาษีมูลค่าเพิ่มจากยอดรวมของราคาอาหารสองรายการ และผลรวมของภาษีกับยอดรวมของราคาอาหาร เพื่อความสวยงามของโค้ด เราเลยจะเขียนโค้ดเป็น module ย่อยๆ ได้แก่
หากเขียนโค้ดตามที่เราออกแบบไว้จะได้ดังนี้
หมายเหตุ: ให้ผู้อ่านลองสร้างไฟล์ทั้ง 4 ไฟล์ใส่ไว้ในโฟลเดอร์เดียวกันนะครับ
| ไฟล์ app.html |
|
<html>
<head>
<script src="sum.js"></script>
<script src="tax.js"></script>
<script src="app.js"></script>
</head>
</html>
|
| ไฟล์ app.js |
|
var foodPrice1 = 99;
var foodPrice2 = 129;
var totalVat = tax(foodPrice1, foodPrice2);
var totalPrice = sum(foodPrice1, foodPrice2);
var priceWithVat = sum(totalPrice, totalVat);
console.log("VAT 7% = " + totalVat);
console.log("total = " + priceWithVat);
|
| ไฟล์ sum.js |
|
var sum = function (a, b) {
return a + b;
};
|
| ไฟล์ tax.js |
|
var tax = function (a, b) {
var total = sum(a, b);
return total * 0.07;
};
|
พอลองรันหน้าเว็บโดยดับเบิ้ลคลิกที่ไฟล์ app.html ดูจะได้ผลลัพธ์ดังนี้
หมายเหตุ: กรณี Chrome สามารถดูผลลัพธ์อย่างนี้ได้โดยคลิกขวาที่หน้าเว็บแล้วเลือก Inspect
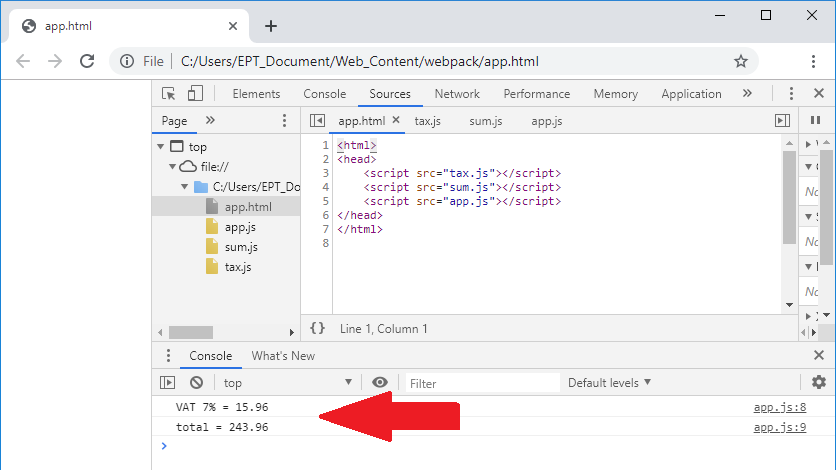
ซึ่งจะเห็นว่าใช้งานได้ถูกต้องไม่มีปัญหาอะไร แต่ๆๆๆ ถ้าเราเขียนไฟล์ app.html เป็นดังต่อไปนี้ล่ะ
***สังเกตว่าลำดับของไฟล์ที่นำเข้ามาสลับกับตอนแรก โดย sum.js มาอยู่ลำดับสุดท้าย
| ไฟล์ app.html |
|
<html>
<head>
<script src="tax.js"></script>
<script src="app.js"></script>
<script src="sum.js"></script>
</head>
</html>
|
พอลองรันหน้าเว็บดูจะได้ผลลัพธ์ดังนี้
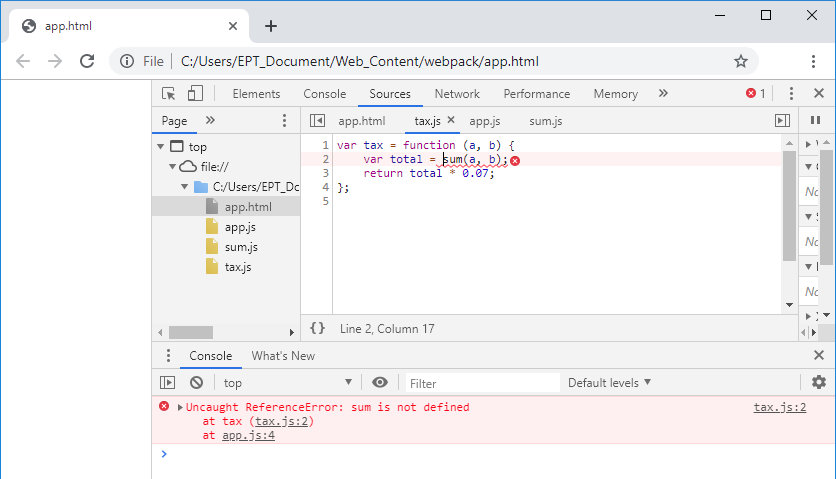
ซึ่งจะเห็นว่าเกิด Error ขึ้นเนื่องจากในบรรทัดที่ 2 ของไฟล์ tax.js ต้องการเรียกฟังก์ชัน sum() แต่มันไม่รู้จัก เนื่องจากเรา include sum.js ไว้หลังสุดนั่นเอง ตรงจุดนี้ล่ะครับที่ webpack จะมาช่วยเรา แล้วมันช่วยอย่างไรล่ะ?
ต้องขออธิบายก่อนว่าในตอนนี้การทำงานของ Application เราเป็นอย่างนี้ครับ
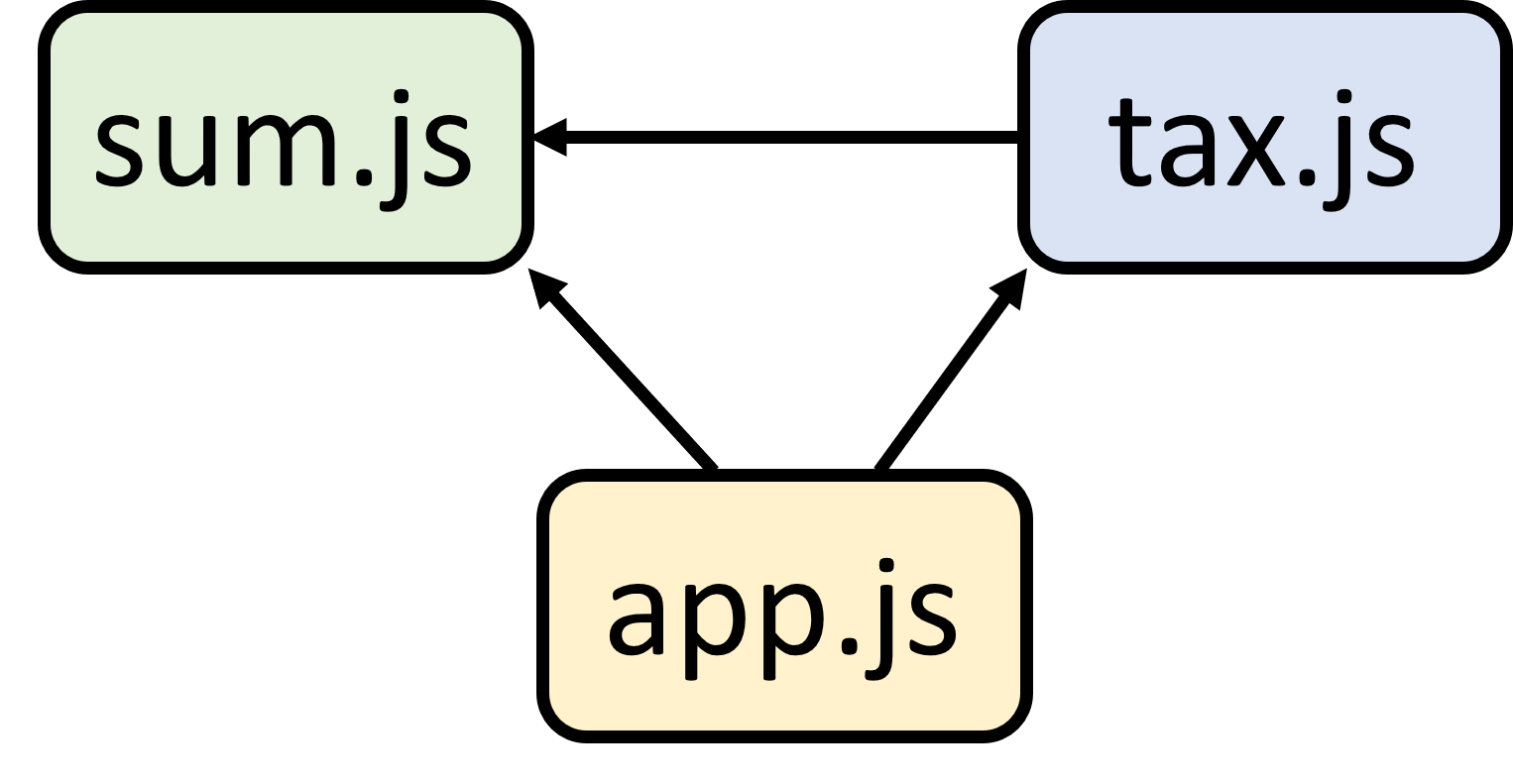
คือ app.js ไปเรียก sum.js และ tax.js ส่วน tax.js ไปเรียก sum.js ทำให้ลำดับการนำเข้าไฟล์มีผลต่อการทำงานของ Application เรา ซึ่งถ้าเราใช้ webpack มาช่วย สิ่งที่จะได้ออกมาจะเป็นอย่างนี้ครับ
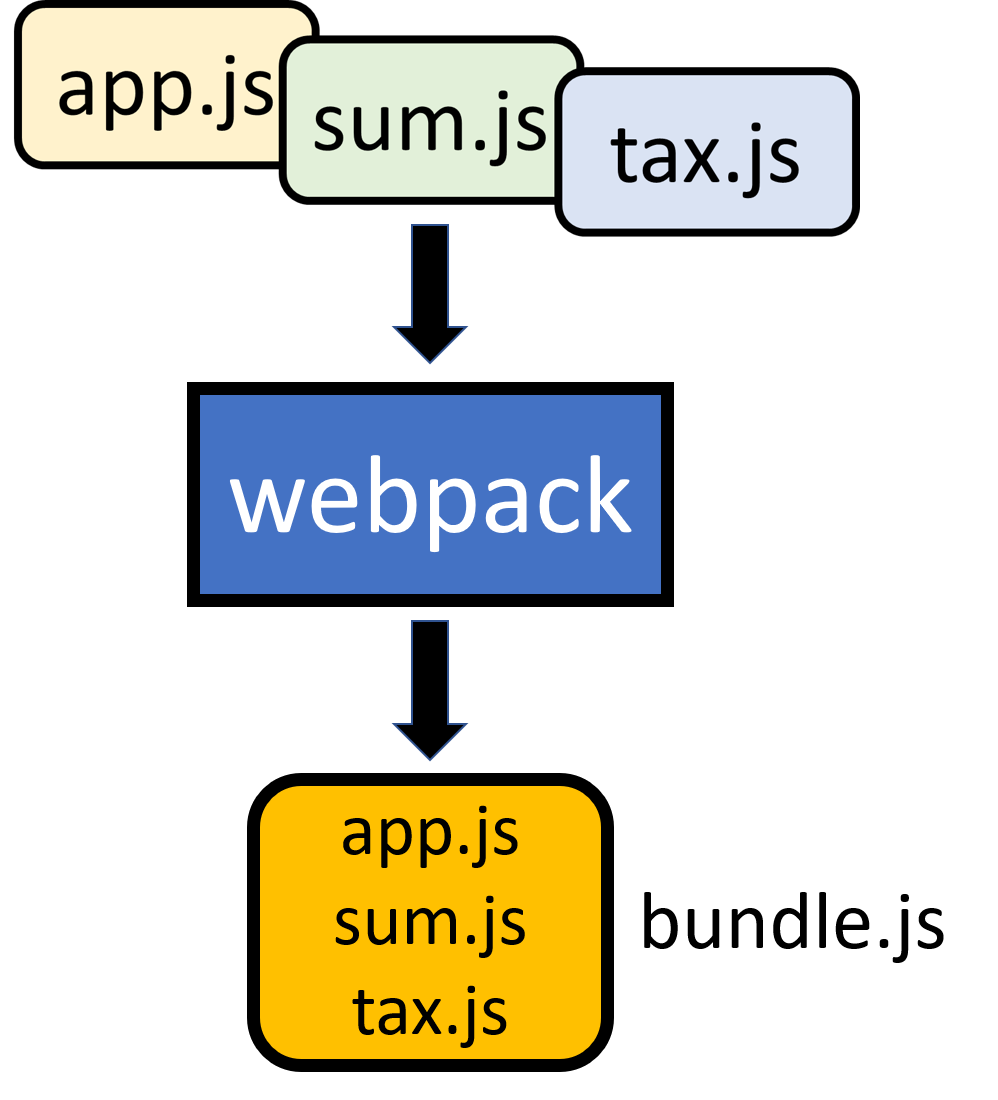
webpack จะช่วยรวม module ให้เรา ทีนี้เราก็ไม่ต้องสนใจลำดับอีกต่อไป ผู้อ่านบางคนอาจจะไม่เห็นประโยชน์ของมัน แต่เชื่อเถิดครับ ถ้าท่านทำ Application ขนาดใหญ่ มี module ย่อยเป็นสิบๆ module แล้วแต่ละ module ก็มีการเรียกอีก module หนึ่ง ถึงตอนนั้นจะเห็นปัญหาอย่างชัดแน่นอน ดังนั้นเรียนรู้ไว้ก่อนไม่เสียหายครับ ว่าแล้วก็มาลองลงมือทำกันเลยดีกว่า
วิธีที่ง่ายที่สุดในการลง webpack คือการใช้ npm ที่เราได้ติดตั้งผ่าน NodeJS ไปแล้วจากบทความ A07_npm01_Intro ดังนั้นในบทความนี้จะถือว่าเครื่องของเรามี npm อยู่แล้วนะครับ ใครยังไม่มีก็ย้อนไปอ่านบทความก่อนๆดูนะครับ
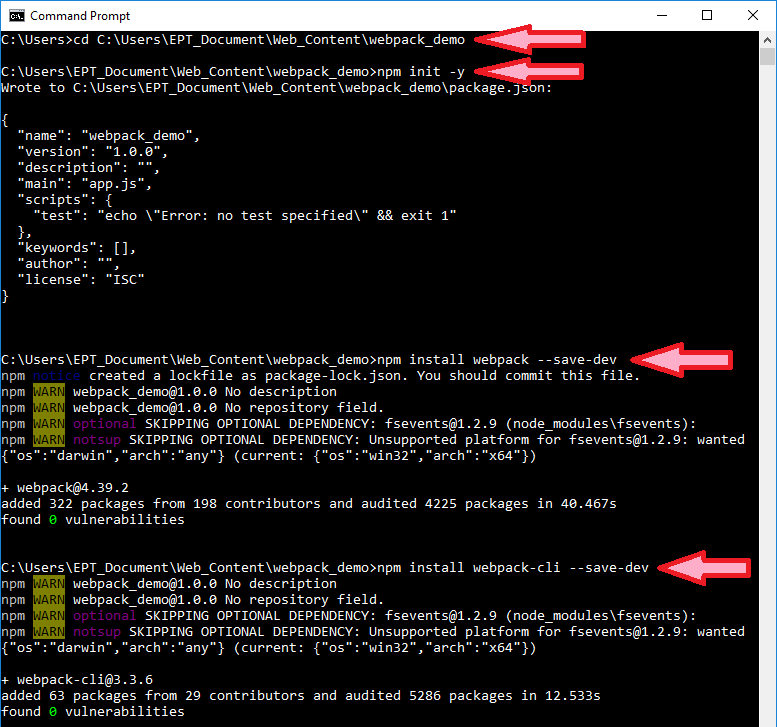
1. เปิด Command Prompt ขึ้นมา แล้วพิมพ์คำสั่ง cd แล้วตามด้วย path ที่ต้องการ เพื่อไปยัง directory ที่เราต้องการลง webpack ในที่นี้จะลงในโฟลเดอร์ชื่อ webpack_demo (จริงๆมีวิธีลงแบบ global แต่จะไม่แนะนำให้ทำครับ)
2. พิมพ์คำสั่ง 3 คำสั่งต่อไปนี้ทีละคำสั่งเพื่อทำการติดตั้ง webpack แบบ local (หมายถึงติดตั้งแค่ใน directory ที่เราต้องการ)
|
npm init -y
npm install webpack --save-dev
npm install webpack-cli --save-dev
|
3. รอจนติดตั้งเสร็จ จะเห็นข้อความเตือนดังนี้ ยังไม่ต้องสนใจครับ และอย่าเพิ่งปิดหน้าต่าง Command Prompt นี้นะครับ
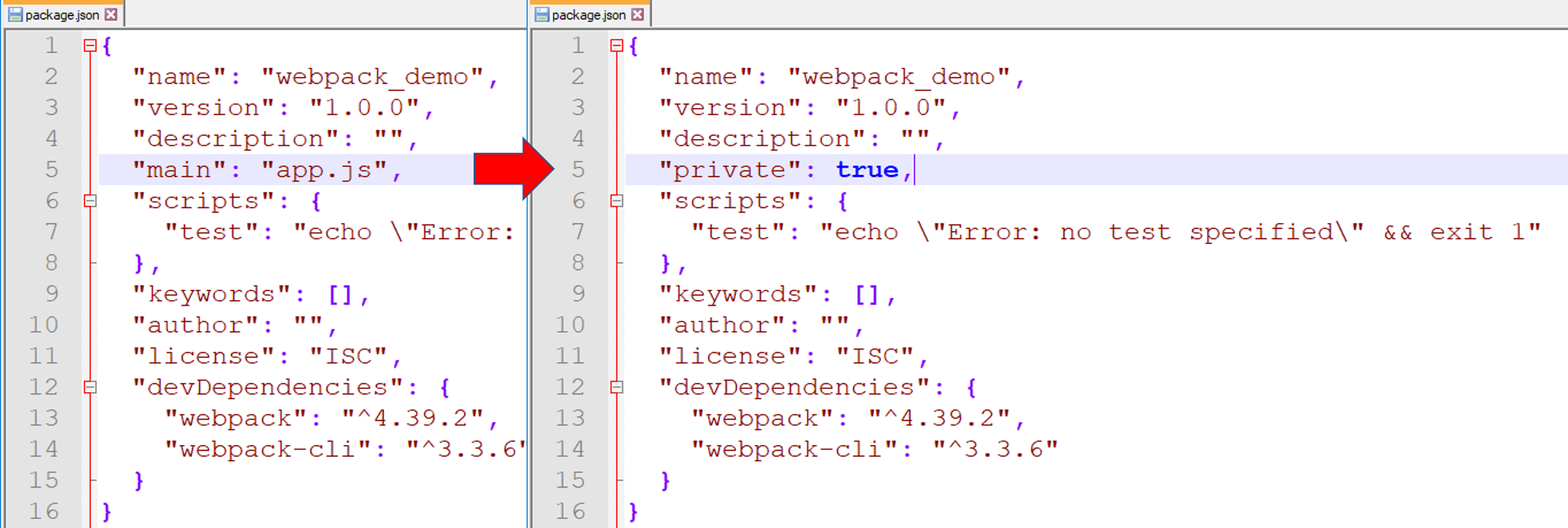
4. หลังจากติดตั้ง webpack เสร็จแล้ว จะเห็นว่าในโฟลเดอร์ webpack_demo มีไฟล์ชื่อ package.json ให้แก้บรรทัด "main": "app.js", เป็น "private": true, เพื่อป้องกันเรา public โค้ดโดยไม่รู้ตัว
5. คราวนี้เราจะมาจัดโฟลเดอร์ไฟล์ที่เราเขียนไว้จากตัวอย่างที่แล้วเพื่อเตรียมสำหรับการ bundle โดยให้สร้างโฟลเดอร์ชื่อ dist และ src เพิ่มไว้ในโฟลเดอร์ที่กำหนดในขั้นตอนที่ 1 (ในตัวอย่างนี้คือโฟลเดอร์ชื่อ webpack_demo) แล้วแก้ชื่อไฟล์จาก app.html เป็น index.html และชื่อไฟล์ app.js เป็น index.js จากนั้นจัดไฟล์เข้าโฟลเดอร์ตามนี้
หมายเหตุ: ขั้นตอนนี้สำคัญมาก ต้องใช้ชื่อและ path ตามนี้เป๊ะๆนะครับ! เนื่องจากตั้งแต่ webpack 4 เป็นต้นมา เราไม่จำเป็นต้องใช้ config file แล้ว ดังนั้นเราสามารถทำให้ webpack ทำงานได้ง่ายๆถ้ามี src/index.js
|
webpack_demo
|- package.json
|- /dist
|- index.html
|- /src
|- index.js
|- sum.js
|- tax.js
|
6. แก้ไฟล์ index.html ให้เรียกแค่ main.js ซึ่งเป็นไฟล์ output ที่จะได้ออกมาหลังจาก bundle เสร็จ นอกจากนั้นก็แก้ไฟล์อื่นๆตามนี้ครับ
| ไฟล์ index.html |
|
<html>
<head>
<script src="main.js"></script>
</head>
</html>
|
| ไฟล์ index.js |
|
import sum from '../src/sum';
import tax from '../src/tax';
var foodPrice1 = 99;
var foodPrice2 = 129;
var totalPrice = sum(foodPrice1, foodPrice2);
var totalVat = tax(foodPrice1, foodPrice2);
var priceWithVat = sum(totalPrice, totalVat);
console.log("VAT 7% = " + totalVat);
console.log("total = " + priceWithVat);
|
| ไฟล์ sum.js |
|
export default function sum(a, b) {
return a + b;
};
|
| ไฟล์ tax.js |
|
import sum from '../src/sum';
export default function tax(a, b) {
var total = sum(a, b);
return total * 0.07;
};
|
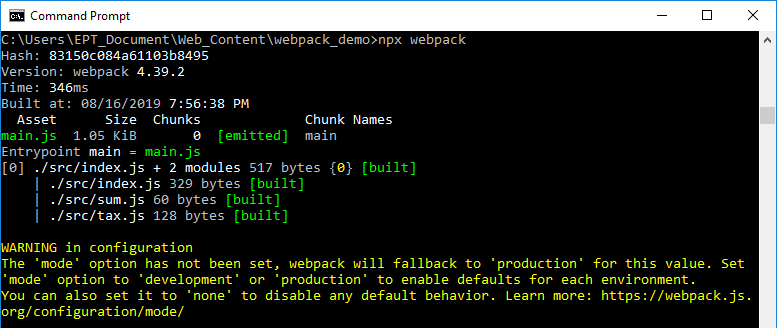
7. กลับไปที่ Command Prompt แล้วพิมพ์คำสั่ง
|
npx webpack |
หมายเหตุ: เมื่อพิมพ์คำสั่งนี้โดยไม่มี config file webpack จะทำงานโดยถือว่า src/index.js เป็น Entry point และจะ generate dist/main.js เป็น output ออกมาให้
8. รอจน build เสร็จ จะขึ้นข้อความแบบนี้ แสดงให้เห็นว่ามันสร้างไฟล์ main.js ให้เราไว้ที่โฟลเดอร์ dist เรียบร้อยแล้วครับ (ไม่ต้องสนใจตรงส่วน WARNING ครับ)

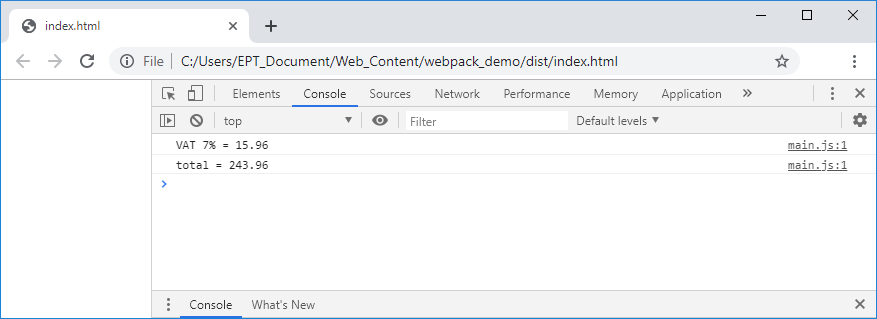
9. ลองดับเบิ้ลคลิกไฟล์ index.html ดู จะได้ผลลัพธ์ตามที่เราต้องการแล้วครับ เย้ๆๆๆ
จบแล้วครับสำหรับเรื่อง Intro to webpack อย่างย่อๆ อาจจะงงๆหน่อยแต่ค่อยๆทำตามทีละขั้น รับรองว่าทำได้แน่นอนครับ
สุดท้ายนี้ถ้าผู้อ่านอยากเรียนรู้เรื่อง JavaScript และเรื่องเกี่ยวกับ Web Programming อย่างลึกซึ้งก็ขอแนะนำคอร์ส Web Programming ของทาง EPT ครับ สามารถดูรายละเอียดคอร์สได้โดยคลิกที่นี่ หรือติดต่อได้ที่ 085-350-7540
แล้วพบกันใหม่บทความหน้าครับ
[1] https://webpack.js.org/
[2] https://webpack.js.org/guides/getting-started/
Tag ที่น่าสนใจ: webpack static_module_bundler javascript module_bundling web_development programming module_loading application_development front-end_development javascript_bundler webpack_configuration
หากมีข้อผิดพลาด/ต้องการพูดคุยเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับบทความนี้ กรุณาแจ้งที่ http://m.me/Expert.Programming.Tutor
085-350-7540 (DTAC)
084-88-00-255 (AIS)
026-111-618
หรือทาง EMAIL: NTPRINTF@GMAIL.COM
