ในบทความก่อนหน้านี้ เราได้รู้จักกับ Server และพวกพ้องที่เกี่ยวข้องกับอินเตอร์เน็ตไปแล้วจำนวนหนึ่ง แต่ถ้าเราเริ่มต้องเขียนโปรแกรมที่เกี่ยวกับเว็บไซต์แล้วสิ่งที่หลายคนน่าจะเคยเห็นผ่านตามาบ้างคือสิ่งที่เรียกว่า API หรืออาจจะเคยได้ยินคนบอกว่า “ให้ส่ง API ไปที่กูเกิ้ลสิ” หรือ “ยิง API ไปที่เฟสบุ๊คสิ” สำหรับคนที่ยังไม่รู้ว่า API คืออะไรกันแน่ ก็ลองมาทำรู้จักกันครับ
API ย่อมาจาก Application Programming Interface ซึ่งเป็นเรื่องที่กว้างมากครับ แต่ถ้าให้อธิบายง่ายๆก็คือ API เป็นวิธีที่คอมพิวเตอร์ใช้คุยกันครับ อาจจะเป็นคุยกันระหว่างโปรแกรมภายในเครื่องเดียวกันเอง หรือคุยกับคอมพิวเตอร์เครื่องอื่นผ่าน Internet protocol เช่น HTTP ก็ได้
ถ้าเปรียบกับคน การส่ง API ไปก็เหมือนเราโทรศัพท์ไปหาร้านขายข้าวแกงหน้าปากซอยแล้วสั่งข้าวไข่เจียว 1 กล่องพร้อมบอกให้มาส่งให้ที่บ้านด้วย แล้วเราก็นั่งรอข้าวไข่เจียวที่เขาจะส่งมาให้หรือก็คือ response นั่นเอง แต่การส่ง API จะยากกว่าการโทรไปสั่งข้าวไข่เจียวอยู่สักหน่อยตรงที่ว่าเราจะต้องสั่งให้ถูกต้องตามแบบฟอร์มเป๊ะๆ มิเช่นนั้นคนขายข้าวแกงจะไม่ทำให้เรา เช่น ร้านข้าวแกงหน้าปากซอยมีแบบฟอร์มคือ เวลาสั่งต้องสั่ง ชื่ออาหาร ตามตัวเลข (1,2,3,...) ตามด้วยหน่วย (กล่อง) ดังนั้นเราก็ต้องสั่งว่า “ข้าวไข่เจียว 1 กล่อง” เท่านั้นจึงจะได้รับข้าวไข่เจียว เราไม่สามารถสั่งว่า “ข้าวไข่เจียวกล่องหนึ่ง” หรือ “ข้าวไข่เจียว 1” หรืออะไรก็ตามที่ผิดไปจากแบบฟอร์มที่กำหนดได้ครับ
A: อ่าน Document ของ xxx ครับ คำตอบนี้ผมไม่ได้กวนตีนนะครับ หลายคนชอบมาถามว่าไม่เข้าใจ API เลย คือเรื่องนี้ผมก็ช่วยไม่ได้ครับ เราต้องอ่าน Document กันเอาเอง เพราะ API ของแต่ละที่มันก็ไม่เหมือนกันขึ้นกับคนออกแบบหรือโปรแกรมเมอร์ที่เขียนล้วนๆเลยครับ มาดูตัวอย่างกัน
สมมติว่าเราอยากทำเว็บตัดบัตรเครดิตด้วย Omise ก่อนอื่นเราก็ไปดู document ก่อนเลยครับว่า API ของเขามีรูปแบบอย่างไร โดยเข้าไปที่ https://www.omise.co/th/docs ซึ่งจาก Document จะมีตัวอย่างของการเรียก API ด้วยคำสั่ง curl ผ่าน Command Line โดยมีรูปแบบดังนี้
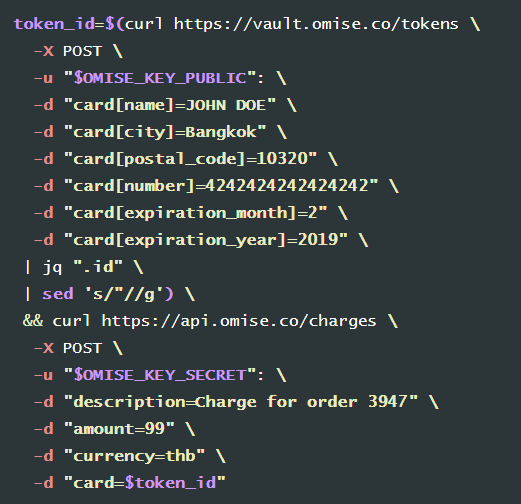
จากรูปแบบด้านบนจะเห็นว่ามีโค้ดอยู่สองชุด ชุดแรกใช้สำหรับสร้าง token โดยต้องใส่ public key ที่เราได้มาจาก omise และข้อมูลบัตรเครดิตต่างๆตามรูปแบบที่กำหนด ส่วนชุดที่สองเป็นการตัดบัตรเครดิต โดยต้องใส่ secrect key ที่เราได้มาจาก omise, จำนวนเงิน, สกุลเงิน และ token ที่ได้มาจากโค้ดชุดแรก แค่พิมพ์ตามนี้ก็จะตัดเงินจากบัตรเครดิตได้เลยครับ
สมมติเราต้องการเรียกใช้ Google Map ในเว็บไซต์ที่เราเขียนเอง เราสามารถเรียกใช้งานได้ฟรี (ตามเงื่อนไขที่ google กำหนด) ผ่าน API ที่ google กำหนดไว้โดยต้องมี gmail ก่อน แล้วเข้าไปขอ API key จาก https://cloud.google.com/console/google/maps-apis/overview แล้วจึงเรียกใช้งานผ่าน JavaScript โดยจะต้องใส่ API key ที่ขอมานี้ทุกครั้งที่มีการ request map ผ่านทาง JavaScript ตามรูปแบบนี้

จากสองตัวอย่างข้างบน จะเห็นว่ารูปแบบ API ไม่เหมือนกันเลยใช่ไหมครับ ดังนั้นถ้าต้องการจะใช้ API ของอะไรจึงต้องอ่าน Document ของสิ่งนั้นให้ดีครับ
สำหรับบางคนที่ยังไม่เห็นว่าจะเอา API ไปใช้ประโยชน์อย่างไรในชีวิตจริง ผมจะขอยกตัวอย่างดังนี้ครับ
ตัวอย่าง1: สมมติเราต้องการทำ Application เรียกรถแท็กซี่แบบ Grab เราก็คงไม่มานั่งทำแผนที่หรือระบบจ่ายเงินเองใช่ไหมครับ สิ่งที่เราสามารถทำได้ง่ายๆก็คือ จ่ายเงินผ่าน API ของธนาคาร หรือ Payment Gateway ต่างๆ และใช้ Google Map ผ่าน API ของ Google Map โดย Google Map ก็จะใช้ API เพื่อจะได้รู้ตำแหน่งของโทรศัพท์ที่กำลังใช้งานอยู่ด้วย
ตัวอย่าง2: สมมติเราต้องการทำ Application อะไรสักอย่างที่ต้องการรู้ตำแหน่งของรถเมล์ทั้งหมดที่กำลังวิ่งอยู่แบบ real-time เราก็คงไม่ไปขอรถเมล์ทุกคันติด GPS ใช่ไหมครับ วิธีที่ดีที่สุดที่เราควรจะทำก็คือ ใช้ API เพื่อขอข้อมูลจาก Traffy (โปรเจกต์หนึ่งของ Nectec) ซึ่งมีข้อมูลหลายอย่างให้เราเอาไปต่อยอดได้ เช่น ข้อมูลของสายรถเมล์ทั้งหมด ข้อมูลและตำแหน่งป้ายรถเมล์ ข้อมูลเวลาที่รถเมล์จะถึงป้าย และข้อมูลป้ายรถเมล์ที่รถสายนั้นๆวิ่งผ่าน และแน่นอนว่าสิ่งที่จำเป็นต้องใช้ประกอบอีกอย่างก็คือแผนที่ครับ ไม่งั้นผู้ใช้งานก็คงงงว่ารถเมล์มันอยู่ที่ไหนกันแน่ ซึ่งเราก็สามารถใช้ Google Map ได้โดยเรียกผ่าน API ครับ
สุดท้ายนี้ถ้าผู้อ่านอยากเรียนรู้เรื่องเกี่ยวกับ Web Programming อย่างลึกซึ้งก็ขอแนะนำคอร์ส Web Programming ของทาง EPT ครับ สามารถดูรายละเอียดคอร์สได้โดยคลิกที่นี่หรือติดต่อได้ที่ 085-350-7540
แล้วพบกันใหม่บทความหน้าครับ
Tag ที่น่าสนใจ: api application_programming_interface web_programming document omise google_map payment_gateway gps traffy nectec
หากมีข้อผิดพลาด/ต้องการพูดคุยเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับบทความนี้ กรุณาแจ้งที่ http://m.me/Expert.Programming.Tutor
085-350-7540 (DTAC)
084-88-00-255 (AIS)
026-111-618
หรือทาง EMAIL: NTPRINTF@GMAIL.COM
